
Introduction
"Easy to Understand! Embedded Fonts" is a blog that explains the basics and terminology of embedded fonts. In this issue, we have summarized an explanation of character sets and character codes, a list of common codes, and points to consider when considering fonts.
Character set
A character set is a set of characters that is defined so that characters and symbols can be displayed and exchanged on a computer.
Representative character sets
Japanese Character Set
Official standards (JIS: Standards established by the Japanese Industrial Standards (formerly the Japanese Industrial Standards))
- JISX0201: 158 characters (JIS half-width characters)
- JISX0208: 6,879 characters (JIS non-kanji, level 1/level 2 kanji)
- JISX0213: 11,223 characters (JISX0208 plus level 3 and 4 kanji characters)
Standards established by specific companies or organizations
●A character set defined by Adobe Systems for Japanese DTP.
- Adobe-Japan1-3: 9,354 characters
- Adobe-Japan1-4: 15,444 characters
- Adobe-Japan1-5: 20,317 characters
- Adobe-Japan1-6: 23,058 characters
●Microsoft's Windows character set
- Microsoft standard character set (Windows31J): 7,881 characters
JISX0208, JISX0201, NEC special characters, NEC selected IBM extended characters, IBM extended characters
*This is the Japanese character set provided by Morisawa for embedded use.
External character set
Some characters are not included in the standard character set specifications, but are standardized for specific purposes.
Below is a typical external character set (ARIB external characters). These are Japanese external characters required for digital broadcasting applications in addition to the characters specified in the JIS standard, and are standardized by the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB).
Major ARIB standards
- ARIB STD-B24: Data broadcasting coding and transmission standards for digital broadcasting
- ARIB STD-B3: Operational standard for FM multiplex broadcasting
- ARIB STD-B62: Multimedia coding standard for digital broadcasting
ARIB external character set
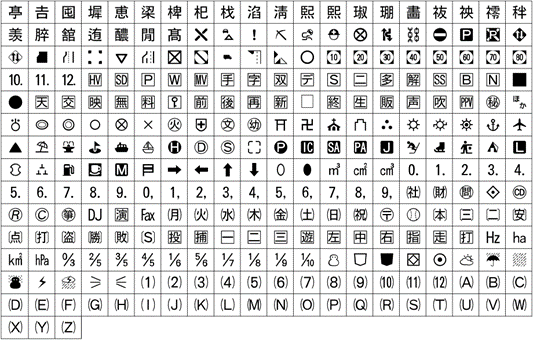
Main products: Digital TVs, recorders, car navigation systems, and other digital broadcasting receivers
Character encoding
A character code is a unique number (character code) assigned to each character or symbol in order to handle a character set (a collection of characters) on a computer.
*Character set and character code are often understood and used as synonyms.
The following is the standard character code (7-bit ASCII) for data interchange established by ANSI, the United States industrial standard. It was originally a domestic standard in the United States, but is now an international standard (ISO-646) established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
ASCII Code Table
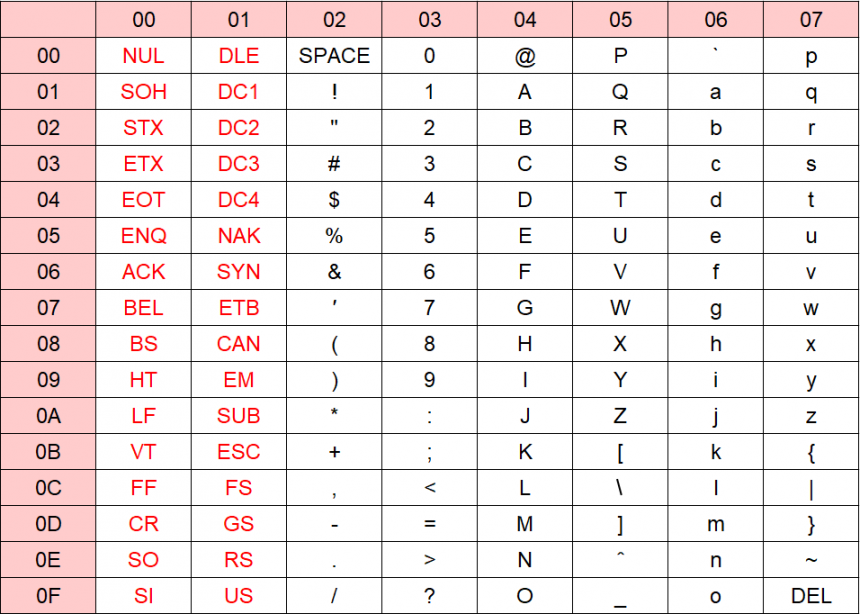
deficitare called control characters, and are characters defined in character codes that are used to operate (control) output devices such as displays, printers, and communication devices. Although they are called "characters," they are also called non-printing characters because they are not output on displays or printers.
1-byte character code
Characters represented by 1 byte (8 bits: 0-255) of data. Representative examples include JISX0201 (ANK characters), which is an extension of ASCII, which contains numbers and alphabets, and includes Japanese half-width characters, and ISO8859, which contains European languages, and is used for languages with a small number of character types.
JISX0201 character code table
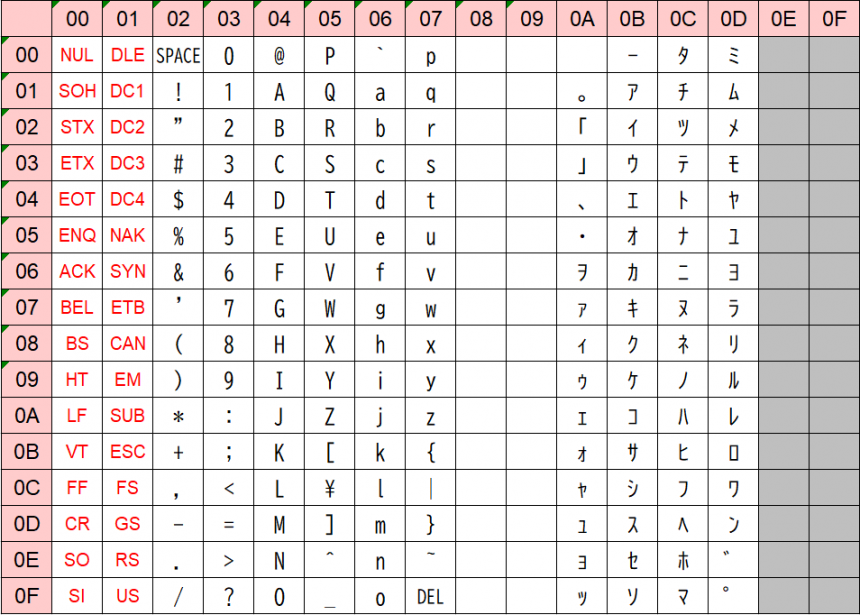
Double-byte character code
A character represented by two bytes (16 bits: 0 to 65,535) of data. It is used in languages such as Japanese, Chinese, and Korean, which have a large number of characters and cannot be expressed in a single byte (0 to 255).
JISX0208 character code table
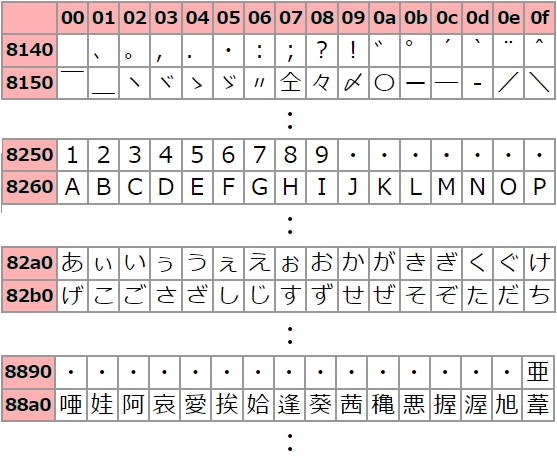
Representative character codes
Shift JIS
A character code that rearranges (shifts) JIS X 0208 to handle a mixture of double-byte and single-byte characters.
Unicode
A character code designed to handle characters from around the world as a common character set
*Latest version 15.0.0 (September 2022): Contains 149,186 characters
The following encoding methods are common:
UTF8: Encoding method expressed in 8-bit units (variable length from 1 to 4 bytes)
UTF16: Encoding method expressed in 16-bit units (fixed length of 2 to 4 bytes)
GB2312
Simplified Chinese character code
It is used in China (mainland China).
GB18030
Chinese character code
It includes simplified and traditional Chinese characters, as well as Chinese characters used in Japan and Korea, and includes GB2312.
Big5
Traditional Chinese character code
It is used in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau.
KSX1001
Korean character code
It includes Hangul and Hanja.
■ Code page
Character codes organized by language. Switch code pages to use each language.
When computers were still relatively unpowered, it was not possible to handle all the characters in the world in one place, so they were recorded separately for each language.
ISO/IEC 8859: A typical single-byte character code. Mainly defines European languages.
| ISO8859-1 (Latin1) | English/German/French/Italian/Spanish/Portuguese/ Dutch/Danish/Swedish/Norwegian/Finland Indian/Icelandic/Irish/Albanian etc. |
| ISO8859-2 (Latin2) | Croatian/Czech/Slovak/Slovenian/Hungarian Polish/Romanian etc. |
| ISO8859-3 (Latin3) | Esperanto/Maltese etc. |
| ISO8859-4 (Latin4) | Estonian/Latvian/Lithuanian etc. |
| ISO8859-5 (Cyrillic) | Russian/Ukrainian/Serbian/Bulgarian/Belarusian /Macedonian etc. |
| ISO8859-6 (Arabic) | Arabic |
| ISO8859-7 (Greek) | Greek |
| ISO8859-8 (Hebrew) | Hebrew |
| ISO8859-9 (Latin5) | Turkish |
| ISO8859-10 (Latin6) | Inuit/Greenlandic/Sami/Lappish, etc. |
| ISO8859-11 | Thai |
| ISO8859-14 (Latin8) | Welsh/Gaelic/Celtic etc. |
WindowsCodePage (CP): Defined by Microsoft for use with Windows
| CP932 | Japanese (ShiftJIS) |
| CP936 | Simplified Chinese (GB2312) |
| CP949 | Korean (KSC5601:1987) |
| CP950 | Traditional Chinese (Big5) |
| CP1252 | English/German/French/Italian/Spanish/Portuguese/Dutch/ Swedish/Finnish/Danish/Norwegian etc. *ISO8859-1 includes some additional characters such as the "€" symbol. |
| CP1250 | Czech, Slovak/Polish/Romanian/Hungarian/Slovenian Croatian, etc. |
| CP1251 | Russian/Ukrainian/Serbian/Bulgarian/Belarusian/Macedonian etc. |
| CP1253 | Greek |
| CP1255 | Hebrew |
| CP1256 | Arabic |
| CP1257 | Estonian/Latvian/Lithuanian etc. |
| CP1258 | Vietnamese |
| CP874 | Thai |
encoding
This refers to converting data based on certain rules, and in this case it refers to assigning each character to a specific character code.
When considering fonts, please check which language, character set, and character code you require.
- Required languages (supported countries): [Example] Japanese, English, Germany, France
- Required character set: [Example] JISX0208, ISO8859-1
- Character code: [Example] Unicode (UTF16)
The required character set may vary depending on how you use the service, such as whether or not you enter data when using it, so please contact us with your specific usage needs.
This concludes our explanation of character sets and character codes.
If you have any questions, please contact us directly by email.

Contact
Morisawa Corporation Sales Innovation Department salesinnovation@morisawa.co.jp